With the development of the photovoltaic industry, the ability of inverters to accept grid dispatch has become a focal point of industry attention. String inverters provide flexible regulation of both active and reactive power. The active power load factor is configurable from 0 to 100%, with an optional 1.1 times active power overload output capability. For reactive power, whether in capacitive or inductive modes, the maximum reactive power load factor reaches 70% of the Voltage. The power factor setting range is from 0.8 leading to 0.8 lagging. Multiple reactive power modes are available to accommodate the diverse requirements of various power plants. The inverters accept and fully comply with dispatch commands from the grid, ensuring full satisfaction of grid connection and control requirements.
Active Power Control Inverters feature three active power (real usable energy) control modes, as follows:
1) Active Power Load Rate Mode:
The machine can limit its active power (usable electrical output) by receiving an active power percentage command, aligning with power plant dispatch requirements.
2) Overfrequency Derating Mode
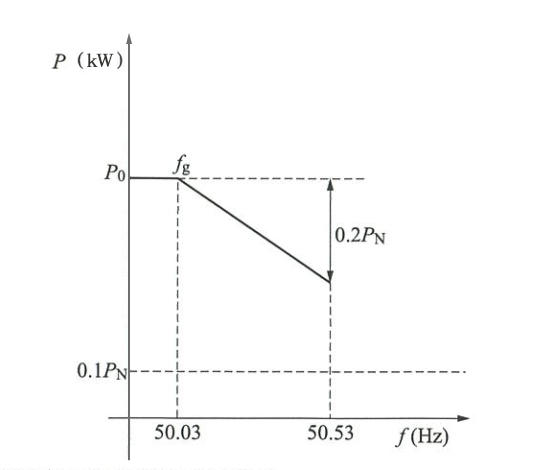
When the overfrequency derating mode is enabled, the inverter adjusts its output power in response to changes in grid frequency. As grid frequency increases, the inverter reduces its active power output. This is done through active power control. The frequency derating curve is shown below:
Frequency Derating Requirement Curve
The overfrequency derating starts at 50.03Hz, with a default derating slope of 40% per Hz. The maximum derating limit can be set to 20% of the rated power. Overfrequency derating requirements comply with NB/T 32004-2018 standards and offer a flexible configuration to meet the needs of power plants.
3) Grid High-Voltage Derating Mode
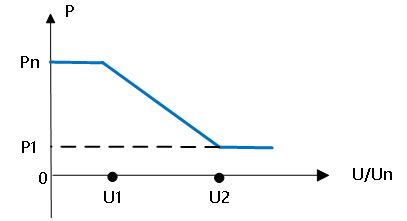
Inverters can also be configured for grid high-voltage derating mode. By setting a high-voltage derating point, the unit automatically reduces power output based on grid voltage. This proactive derating mitigates the risk of excessive grid voltage.
Grid High-Voltage Load Shedding Curve Diagram
As shown in the grid high-voltage derating curve above, U1 (the low point of high-voltage derating) and U2 (the high point of high-voltage derating) can be set to enable machine derating at different voltage points, yielding an appropriate derating slope curve. Point P1 can be set as the minimum power during grid high-voltage derating.
Reactive Power Control
To meet diverse grid requirements for reactive power regulation, string inverters offer six reactive power control functions: Fixed Power Factor (PF), Fixed Reactive Power Ratio (Q(%)), Voltage-Based Reactive Power Regulation (Q(U)), Active/Reactive Power Regulation (Q(P)), Default PF Curve (Q(P-PF)), and Reactive Power Value Regulation (Q(Value)). A single unit provides reactive power adjustment capability within a maximum range of -70% Pn to 70% Pn.
String inverters comply with standards NB/T 32004-2018 and GB/T 37408-2019.
1) Fixed Power Factor (PF)
Inverters control reactive power output by setting a fixed power factor. The power factor is adjustable within the ranges of -1 to -0.8 and 0.8 to 1. The following diagram illustrates the PF setting range for a unit with a rated power Pn of 150K:
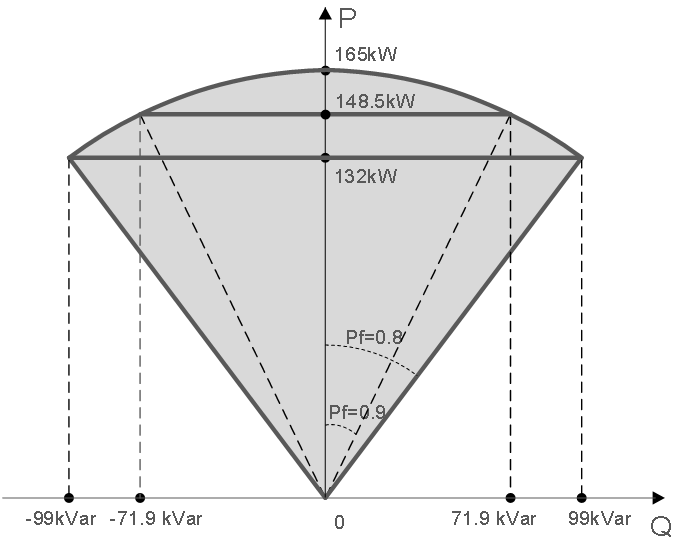
PF Setting Range
The inverter’s rated active power output is Pn=150kW, maximum active power output is Pmax=165kW, maximum apparent power output is Sn=165kVA, and maximum reactive power output ranges from -99kVA to 99kVA.
1) Fixed Reactive Power Ratio (Q(%))
The inverter controls reactive power output by setting a fixed percentage of reactive power. The adjustable range is -70% Pn to 70% Pn. For example, with a rated power of 150kW, the maximum overload power is 165kW, and the maximum reactive power output range is -115.5 kVA to 115.5 kVA.
2) Voltage-dependent reactive power regulation (Q(U))
Inverters achieve a variable reactive power output in response to grid voltage changes by adjusting voltage-reactive power curves. The QU curve defines four voltage points (U1, U2, U3, U4) and two reactive power points (Q1, Q2). Configuring these points establishes distinct voltage-reactive power relationship curves. An example QU curve is shown below:
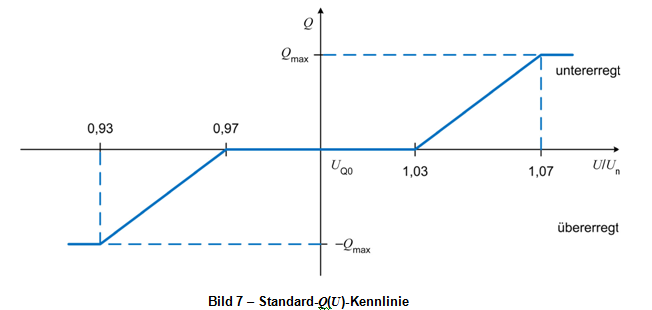
Voltage-Reactive Power (QU) Curve
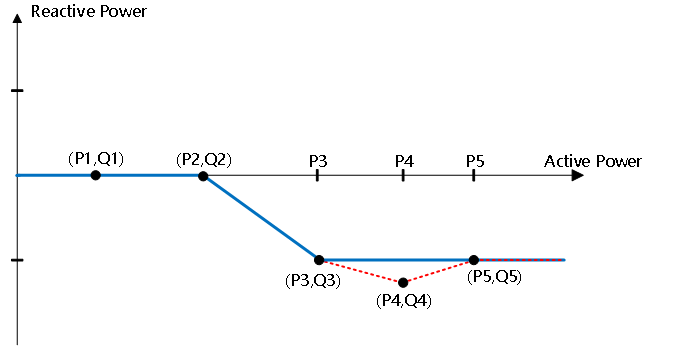
4) Active-Reactive Power Regulation (Q(P))
The inverter can achieve variable reactive power output in response to active power by configuring an active-reactive curve. The QP curve supports up to five active points (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) and five reactive points (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, Q5). Configuring these points enables different active-reactive relationship curves. The following is an example QP curve:
Active-Reactive Power Regulation QP Curve
5) Default PF Curve (Q(P-PF))
The inverter can achieve variable output power factor with active power by configuring a default PF curve. This curve supports three active power points (P1, P2, P3) and one final target power factor point (PF1). Configuring these points enables different active power-power factor relationship curves. The following is an example default PF curve:
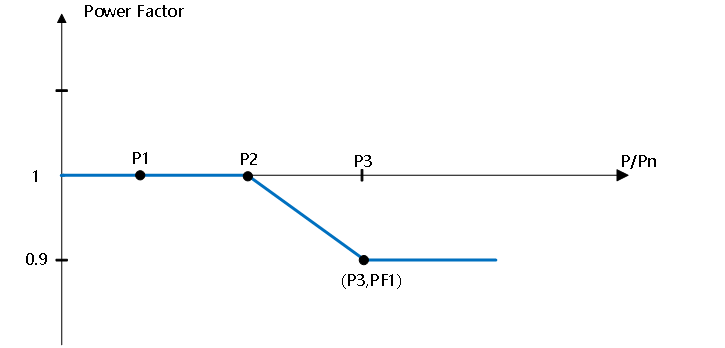
Default PF Curve
6) Reactive Power Value Adjustment (Q(Value))
The inverter can control reactive power output by setting a fixed reactive power value. The maximum adjustable range for reactive power is -66% to 66% of the nominal power (Pn). Taking a machine with a rated power of 150kW as an example, its maximum overload power is 165kW, and the maximum reactive power output range is -99 kVA to 99 kVA. Through the above active and reactive power modes, the inverter offers highly flexible output regulation, providing multiple options for grid support at power plants. This demonstrates the inverter’s comprehensive consideration of user requirements, with active and reactive power control capabilities that are more extensive than comparable products.
Winpower Cable is a provider of connection solutions for the new energy system.
Our main products: Solar PV Cable, Energy Storage Cable, EV Charging Cable, Solar PV Cable Harness, Energy Storage Cable Harnesses, and Automotive Cable.
Winpower Cable has passed UL, TUV, VDE, CE, CSA,CQC Certification.
Our main markets: United States, Europe, Middle East, Southeast Asia. And we have 13 years of export experience.
Post time:
Sep-24-2025